Newton's Laws of Motion
by Laura Wahlrab
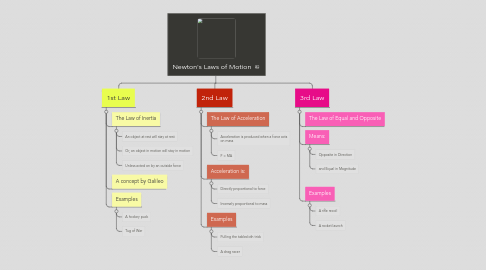

1. 1st Law
1.1. The Law of Inertia
1.1.1. An object at rest will stay at rest
1.1.2. Or, an object in motion will stay in motion
1.1.3. Unless acted on by an outside force
1.2. A concept by Galileo
1.3. Examples
1.3.1. A hockey puck
1.3.2. Tug of War
2. 2nd Law
2.1. The Law of Acceleration
2.1.1. Acceleration is produced when a force acts on mass
2.1.2. F = MA
2.2. Acceleration is:
2.2.1. Directly proportional to force
2.2.2. Inversely proportional to mass
2.3. Examples
2.3.1. Pulling the tablecloth trick
2.3.2. A drag racer
3. 3rd Law
3.1. The Law of Equal and Opposite
3.2. Means:
3.2.1. Opposite in Direction
3.2.2. and Equal in Magnitude
3.3. Examples
3.3.1. A rifle recoil
3.3.2. A rocket launch
