1. Pre-Structural
1.1. No pre-concieved knowledge of concept
1.1.1. Requires Collaborative provocations to tune in
1.1.2. Enhanced PYP/ASSESSMENT:The fundamental purpose of all assessment is to understand where the student is at any given time, and over time, in their learning. It involves the gathering and analysis of information about student learning to inform teaching practice. It identifies what students know, understand, can do, and feel at different stages in the learning process.
1.1.3. Personal reflection: Assessment implications apply across all areas as the point of need for each student is different based on where they fit on the Taxonomy.
2. Relational
2.1. Students appreciates parts and how they relate to the whole, connects ideas
2.2. Deeper level understanding
2.2.1. Enhanced PYP/INQUIRY:An explicit focus on agency–voice, choice and ownership–will encourage active, inquiring students to take responsibility for their own learning. The planner has been redesigned to include student agency through inquiry, action and reflection. Flexible, open-ended time-frames for units of inquiry allow for more sustained, in-depth inquiry.
2.3. Personal Reflection: Looking at how best to achieve this deeper understanding, how does inquiry move from guided to student led and increased student efficiency as they move through the taxonomy
3. Uni- Structural
3.1. Student shows a concrete understanding of one component of a concept
3.2. surface level understanding
3.3. .
3.3.1. .
3.3.1.1. Enhanced PYP/EARLY LEARNER: The four central features of the early years are: ● Play as the primary vehicle for inquiry, with planning for uninterrupted time for play ● Building strong relationships with students and their families ● Creating and maintaining responsive/interactive learning spaces for play ● Offering many opportunities for symbolic exploration and expression.
3.3.2. Personal Reflection: With play as a central part of learning in the early years, the constructiveness of these experiences allow for students to move through the taxonomy.
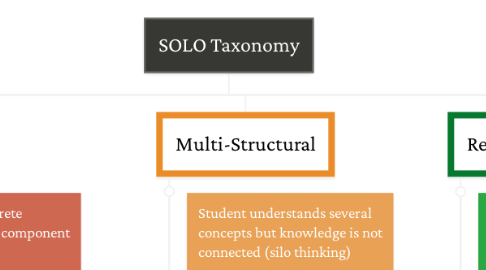
4. Multi-Structural
4.1. Student understands several concepts but knowledge is not connected (silo thinking)
4.2. surface level understanding
4.2.1. Enhanced PYP/ATL: The development of these higher order thinking skills frequently identified as crucial in supporting students to effectively navigate challenges and complexities effectively inside and outside of school.
4.2.2. Personal reflection: Point of need explicit teaching and implicit experiences related to the relevant sub skills has prominence as you move through a conceptual understanding taxonomy. Which sub skills at what time feature throughout any given inquiry? Matching the skills with the experience
5. Extended Abstract
5.1. Understanding is transferable, students can conceptualize at level that is beyond explicit teaching
5.2. Deeper level understading
5.2.1. Enhanced PYP/EXHIBITION: Schools starting with developing a guided exhibition move towards a student-led exhibition as their experience with the PYP deepens and their expectation for student agency increases.
