PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Lucero Sánchez Cotaにより
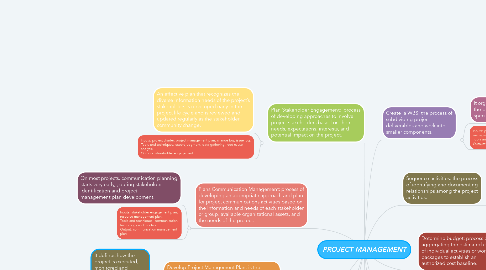

1. Develop Project Management Plan: is the process of defining, preparing, and coordinating all plan components and preparing, all plan components, consolidating them into an integrated project management plan
1.1. It defines how the project is executed, monitored and controlled, and closed.
1.2. Inputs: project charter, outputs from other processes. Tools and techniques: checklist, focus group, brainstorming. Outputs: project management plan.
2. Develop the schedule: is the process of analyzing activity sequences, durations, resource requirements, and schedule constraints to create a schedule model for project execution and monitoring and controlling.
2.1. Schedule development can requiere the review of duration estimates, resources, schedule reserves, among others.
2.2. Inputs: activity list, activity attributes. Tools and techniques: critical path method, schedule network analysis. Outputs: schedule baseline, project schedule.
3. Quality indicators: process of identifying quality requirements and/or standards for the project and its deliverables, and documenting how the project will demonstrate compliance with quality requirements and/or standards.
3.1. Quality planning should be performed in parallel with the other planning processes
3.2. Inputs: risk register, stakeholder engagement plan. Tools and techniques: benchmarking, brainstorming. Outputs: quality management plan, quality metrics.
4. Plans Communication Management: process of developing an appropriate approach and plan for project communications activities based on the information and needs of each stakeholder or group, available organizational assets, and the needs of the project.
4.1. On most projects, communication planning starts very early, , during stakeholder identification and project management plan development.
4.2. Inputs: stakeholder engagement plan, resource management plan. Tools and techniques: communication technology and models. Output: communication management plan
5. Plan Procurement Management: process of documenting project procurement decisions, specifying the approach and identifying potential sellers.
5.1. Defining roles and responsibilities related to procurement should be done early in the Plan Procurement Management fining roles and responsibilities related to procurement should be done early in the Plan Procurement Management process. The project manager should ensure that the project team is staffed with procurement expertise at the level required for the project.
5.2. Inputs: project charter, scope management plan, milestone list. Tools and techniques: market research, make-or-buy analysis. Output: procurement management plan, source selection criteria
6. Plan Stakeholder Engagement: process of developing approaches to involve project stakeholders based on their needs, expectations, interests, and potential impact on the project.
6.1. An effective plan that recognizes the diverse information needs of the project’s stakeholders is developed early in the project life cycle and is reviewed and updated regularly as the stakeholder community change.
6.2. Inputs: project charter, project management plan, change log, issue log. Tools and techniques: expert judgment, data gathering, root cause analysis. Outputs: stakeholder engagement.
7. Create a WBS: the process of subdividing project deliverables and work into smaller components.
7.1. It organizes and defines the total scope of the project and represents the work specified in the current approved project.
7.2. Inputs: project scope statement, project management plan. Tools and techniques: decomposition. Outputs: WBS, work package.
8. Develop Project Charter: the process of developing a document that formally authorizes the existence of a project
8.1. It provides a direct link between the project and the strategic objectives of the organization, creates a formal record of the project, and shows the organizational commitment to the project.
8.1.1. Business documents
8.1.2. Agreements
8.1.3. Environmental Factors
8.1.4. Organizational Process Assets
8.1.5. Data gathering
