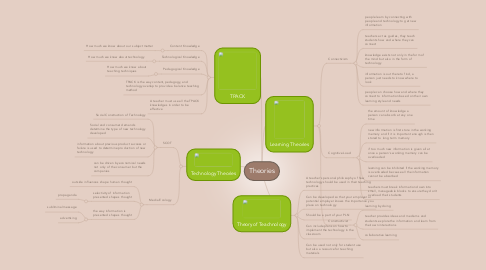
1. Technology Theories
1.1. SCOT
1.1.1. Social Construction of Technology
1.1.2. Social and consumer demands determine the type of new technology developed
1.1.3. information about previous product success or failure is used to determine production of new technology
1.1.4. can be driven by economical needs not only of the consumer but the companies
1.2. Media Ecology
1.2.1. outside influences shape human thought
1.2.2. selectivity of information presented shapes thought
1.2.2.1. propaganda
1.2.3. the way information is presented shapes thought
1.2.3.1. subliminal message
1.2.3.2. advertising
2. Theory of Teachnology
2.1. A teacher's personal philosophy of how technology should be used in their teaching practices
2.2. Can be developed so that your employer or potential employer knows the importance you place on technology
2.3. Should be a part of your PLN
2.4. Can include plans on how to implement the technology in the classroom
2.5. Can be used not only for student use but also a resource for teaching materials
3. TPACK
3.1. Content Knowledge
3.1.1. How much we know about our subject matter
3.2. Technological Knowledge
3.2.1. How much we know about technology
3.3. Pedagogical Knowledge
3.3.1. How much we know about teaching techniques
3.4. TPACK is the way content, pedagogy, and technology overlap to provide a balance teaching method
3.5. A teacher must use all the TPACK knowledges in order to be effective
4. Learning Theories
4.1. Connectivism
4.1.1. people learn by connecting with people and technology to get new information
4.1.2. teachers act as guides, they teach students how and where they can connect
4.1.3. knowledge exists not only in the form of the mind but also in the form of technology
4.1.4. information is out there to find, a person just needs to know where to look
4.1.5. people can choose how and where they connect to information based on their own learning style and needs
4.2. Cognitive Load
4.2.1. the amount of knowledge a person can absorb at any one time
4.2.2. new information is first store in the working memory and if it is important enough is then stored to long term memory
4.2.3. if too much new information is given all at once a person's working memory can be overloaded
4.2.4. learning can be inhibited if the working memory is overloaded because all the information cannot be absorbed
4.2.5. teachers must break information down into small, manageable blocks to ensure they don't overload their students
4.3. Constructivist
4.3.1. learning by doing
4.3.2. teacher provides ideas and mediums and students explore the information and learn from their own interactions
4.3.3. collaborative learning
