1. Plant Cell
1.1. Cell Wall
1.1.1. Only in plant cell
1.1.2. Provides structure and protection for the cell
1.1.3. In outer most "layer" of the cell
1.2. Cell membrane
1.2.1. found in both animal and plant cells
1.2.2. controls what leaves and enters the cell
1.2.3. provides structure/support
1.3. Cytoplasm
1.3.1. a jelly like substance in which all the organelles are suspended
1.3.2. the site of the chemical reactions
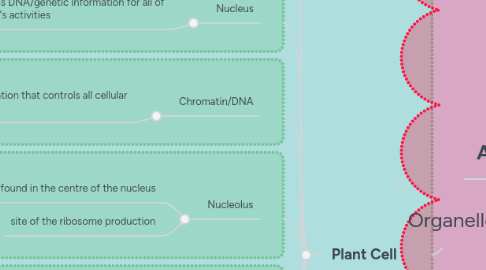
1.4. Nucleus
1.4.1. contains DNA/genetic information for all of the cell's activities
1.5. Chromatin/DNA
1.5.1. genetic information that controls all cellular activity
1.6. Nucleolus
1.6.1. found in the centre of the nucleus
1.6.2. site of the ribosome production
1.7. Ribosomes
1.7.1. responsible for protein synthesis
1.8. Endoplasmic reticulum
1.8.1. a network of tubes for transportation throughout the cell
1.8.2. Rough ER:
1.8.2.1. aids in production of proteins
1.8.3. Smooth ER:
1.8.3.1. aids in production of fats
1.9. Vacuole
1.9.1. storage for the cell
1.9.2. a single central vacuole stores water
1.10. Golgi body
1.10.1. processes and packages materials to be sent out of cell
1.11. Mitochondria
1.11.1. site of cellular respiration
1.11.1.1. turns glucose into energy
1.11.2. aka the "powerhouse of the cell"
1.12. Chloroplasts
1.12.1. only in plant cells
1.12.2. site where photosynthesis occurs
1.12.2.1. makes food/glucose from light energy, carbon dioxide and water
1.12.3. gives plants their green colour
2. The Cell Cycle
3. Interphase
3.1. the cell performs its normal functions
3.1.1. growth
3.1.2. cellular respiration
3.1.3. specialized cell functions
3.1.4. getting ready for mitosis
3.2. longest stage for most cells
3.3. 3 sub phases
3.3.1. G1 - gap 1
3.3.1.1. replication of organelles
3.3.2. S - synthesis
3.3.2.1. replication of DNA
3.3.2.1.1. occurs BEFORE cell division
3.3.3. G2 - gap 2
3.3.3.1. preperation for mitosis
3.4. Nucleus contains chromatin
3.5. a pair of centrioles are together at one part of the cell
3.6. Chromosones
3.6.1. all eukaryotic cells store genetic info in chromosomes
3.6.2. each chromosome is composed of a single tightly-coiled molecule of DNA
3.6.2.1. DeoxyriboNucleicAcid
3.6.3. Chromosomes in dividing cells
3.6.3.1. single stranded chromosomes have one chromatid or arm
3.6.3.2. double stranded chromosomes have two chromatids or arms
3.6.3.3. each chromatid is a full set of DNA held together at the centromere
3.6.3.3.1. called sister chromatid
4. Mitosis
4.1. division of the nucleus
4.2. ensues each new cell gets a full set of DNA (the instruction for cell activities)
4.3. 4 stages
4.3.1. prophase
4.3.1.1. chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form visible chromasones
4.3.1.2. nuclear membrane (membrane around the nucleus) and nucleolus breakdown
4.3.1.3. spindle fibres form in cytoskeleton (plant cells) or centrioles (animal cells)
4.3.1.3.1. spindle fibres attach to the centromere of each chromasone
4.3.2. metaphase
4.3.2.1. chromosomes attached to the spindle fibres move to the centre of the cell
4.3.2.2. chromosones are now lined up at the equator
4.3.3. anaphase
4.3.3.1. occurs rapidly
4.3.3.2. spindle fibres contract and pull sister chromatids apart (centromeres separate)
4.3.3.3. chromatids are moved to opposite poles of the cell
4.3.4. telophase
4.3.4.1. chromosones at opposite poles
4.3.4.2. spindle disassembles
4.3.4.3. nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosones
4.3.4.4. nucleolus reappears
4.3.4.5. chromosones uncoil into chromatin
4.3.4.6. essentially the reverse of what happens during prophase
4.3.4.7. two nuclei in one cell
5. Cytokinesis
5.1. division of the cytoplasm
5.2. division of the rest of the cell into two identical daughter cells
5.3. animal cells only
5.3.1. microfilaments form around the cell
5.3.2. microfilaments constrict forming cleavage furrow
5.3.3. the cell is completely lined by the microfilaments and 2 cells form
5.4. plant cells only
5.4.1. following anaphase, carbohydrate rich vesicles form around centre of the cell
5.4.2. vesicles fuse and cell plate starts forming
5.4.3. cell plate is completely formed, two cells are formed
5.5. daughter cells
5.5.1. have the same number of chromasones as each other, and the parent cell from which they were formed
5.5.2. identical to each other, identical to, but smaller than parent cell
5.5.3. must grow to become mature cells
6. Animal Cell
6.1. Cell Membrane
6.1.1. Found in both animal and plant cells
6.1.2. Controls what leaves and enters the cell
6.1.3. Provides structure/support
6.2. Cytoplasm
6.2.1. a jelly like substance in which all the organelles are suspended
6.2.2. the site of the chemical reactions
6.3. Nucleus
6.3.1. contains DNA/genetic information for all of the cell's activities
6.4. Chromatin/DNA
6.4.1. Genetic information that controls all cellular activity
6.5. Nucleolus
6.5.1. found in the centre of the nucleus
6.5.2. site of the ribosome production
6.6. Ribosomes
6.6.1. responsible for protein synthesis
6.7. Endoplasmic reticulum
6.7.1. a network of tubes for transportation throughout the cell
6.7.2. Rough ER:
6.7.2.1. aids in production of protein
6.7.3. Smooth ER:
6.7.3.1. aids in the production of fat
6.8. Vacuole
6.8.1. storage for the cell
6.8.2. multiple smaller vacuoles, store water, waste, etc.
6.9. Golgi body
6.9.1. processes and packages materials to be sent out of the cell
6.10. Mitochondria
6.10.1. site of cellular respiration
6.10.1.1. turns glucose into energy
6.10.2. aka the "powerhouse of the cell"
6.11. Lysosomes
6.11.1. only found in animal cells
6.11.2. contains digestive enzymes to breakdown waste
6.12. Centrioles
6.12.1. only in animal cells
6.12.2. controls the spindle fibres during cell division
