Meiosis
Door morgan mcvay
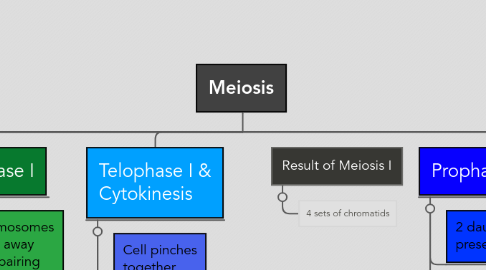

1. Meiosis is the process in which the chromosomes in a parent cell are reduced to half. The process results in four gamete (sex) cells.
1.1. There are many steps in Meiosis: Interphase, Prophase 1, Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, Telophase 1 and Cytokinesis, Prophase 2, Metaphase 2, Anaphase 2, and Telophase 2 and Cytokinesis.
1.2. Before we begin, we have to address Diploid vs. Haploid. The cells going into Meiosis are Diploid, meaning it contains two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. After the meiotic cell cycle, it is Haploid, meaning it has half the number of chromosomes.
2. Interphase
2.1. (2n)
2.2. Nucleus dissapears
2.3. Centrosomes move to opposite sides of cell
2.3.1. A centrosome is an organelle near the nucleus of a cell that contains the centrioles (in animal cells) and from which the spindle fibers develop in cell division.
2.4. Chromosomes become visable
2.5. DNA is copied
3. Prophase I
3.1. Homologous chromosomes pair up
3.2. Cross over occurs
3.2.1. Cross-over is when chromosomes cross over each other and exchange genes
