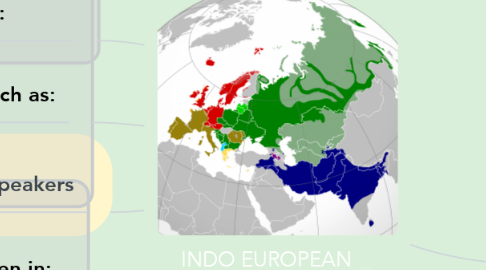
1. Are a large language family native to western Eurasia.
2. Indo-European languages are believed to be derived:
2.1. Proto-Indo-European language
3. Earliest speakers
3.1. Lived around Ukraine
4. Spoken in:
4.1. America
4.2. Europa
4.3. Western and Southern Asia
5. Languages such as:
5.1. Spanish
5.2. French
5.3. Portuguese
5.4. Italian
6. Mind Map, Indo-European Family Languages by katherin Vanessa Pineda Amaya
7. Branches of Indo-European Languages
7.1. Anatolian
7.1.1. Predominated
7.1.1.1. Asian part of Turkey
7.1.1.2. Northern areas of Syria
7.1.2. Anatolian Languages
7.1.2.1. Ancient Anatolian Languages:
7.1.2.1.1. Hittite
7.1.2.1.2. Luwian
7.1.2.1.3. Palaic
7.1.2.2. Late Anatolian Lenguages:
7.1.2.2.1. Carian
7.1.2.2.2. Lycian
7.1.2.2.3. Milyan
7.1.2.2.4. Lydian
7.1.2.2.5. Pisidian
7.1.2.2.6. Sidetic
7.2. Indo-Iranian
7.2.1. Countries with Indo-Iranian Languages
7.2.1.1. Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, India, Iran, Iraq, Maldives, Nepal, South ossetia, Pakistan, Armenia, Syria, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Turkey
7.2.2. Indo-Iranian Lenguages
7.2.2.1. Classification
7.2.2.1.1. Indic Languages
7.2.2.1.2. Iranian Languages
7.2.3. Extension
7.2.3.1. South, Central, Western Asia, South East Europe and the Caucasus
7.3. Greek
7.3.1. Predominant
7.3.1.1. Southernof the Balkans
7.3.1.2. Peloponnese peninsula
7.3.1.3. Aegean Sea
7.3.2. Classification of Dialect
7.3.2.1. Ancient Greek Dialects
7.3.2.1.1. Ionian-Attic
7.3.2.1.2. Doric and Northwest Greek
7.3.2.1.3. Arcado-Cypriot
7.3.2.2. Current Dialects
7.3.2.2.1. Pontic-Cappadocian
7.3.2.2.2. Tsaconic,
7.3.2.2.3. Grecanic
7.3.2.2.4. Grico or Greek Salentino
7.3.3. Countries with Greek Languages
7.3.3.1. Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, France, Turkey, U.S
7.4. Italic
7.4.1. Predominant
7.4.1.1. Italian Peninsula
7.4.2. Italic Languages
7.4.2.1. Faliscan, Sabellic, Umbrian, South Picene, and Oscan
7.4.2.2. Romance languages
7.4.3. Expansion
7.5. Celtic
7.5.1. Classificacion of Celtic Languages
7.5.1.1. Continental Celtic
7.5.1.1.1. The main continental language was Gaulish
7.5.1.2. Insular Celtic
7.5.1.2.1. Irish Gaelic, Scottish Gaelic, Welsh and Breton
7.5.2. The Celtic-speaking tribes spread:
7.5.2.1. Southern Germany, Austria and western Czech Republic, France, Belgium, Spain and the British Isles, northern Italy and southeastern Balkans
7.6. Germanic
7.6.1. Classification of Germanic Languages
7.6.1.1. East Germanic,
7.6.1.2. North Germanic
7.6.1.2.1. Danish, Faroese, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish
7.6.1.3. West Germanic
7.6.1.3.1. Dutch, English, Frisian, and Yiddish
7.6.2. Extension
7.7. Armenian
7.7.1. They settled
7.7.1.1. Lake Van
7.7.2. They could belong to the Balkans or the Iranian group
7.7.3. Countries with Armenian Languages
7.8. Tocharian
7.8.1. Predominated
7.8.1.1. Western China
7.8.1.1.1. Taklamakan Desert
7.8.2. Tocharian Languages
7.8.2.1. Agnean (Tocharian A)
7.8.2.2. Kuchen (Tocario B)
7.8.2.3. Kroränian (Tocharian C)
7.9. Balto-Slavic
7.9.1. Classification
7.9.1.1. Baltic
7.9.1.1.1. Extension:
7.9.1.1.2. Baltic Languages:
7.9.1.2. Slavic
7.9.1.2.1. Extension:
7.9.1.2.2. Slavic Languages:
7.9.2. Countries with Balto-Slavic Languages:
7.9.2.1. Lithuania, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland , Belarus, Ukraine, Russia, Latvia, North Macedonia, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, Germany
7.10. Albanian
7.10.1. Origin of Albanian
7.10.1.1. Descendant of Illyrian
7.10.2. Countries with Albanian Languages:
7.10.2.1. Yugoslavia, Albania,southern Italy, Greece and Republic of Macedonia
