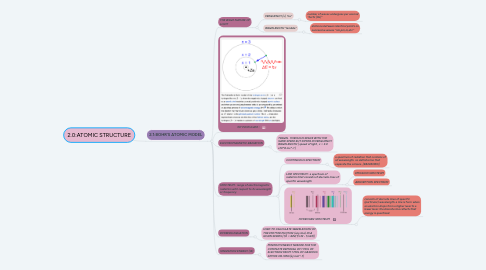
1. 2.1:BOHR'S ATOMIC MODEL
1.1. THE WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT
1.1.1. FREQUENCY [v] "nu"
1.1.1.1. number of waves undergoes per second "hertz [Hz]"
1.1.2. WAVELENGTH "lambda"
1.1.2.1. distance between identical points on successive waves "nm,pm,m,etc"
1.2. 1ST POSTULATE :
1.3. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
1.3.1. TRAVEL THROUGH SPACE WITH THE SAME SPEED BUT DIFFER IN FREQUENCY WAVELENGTH [ speed of light , c = 3.0 x10^8 ms^-1 ]
1.4. SPECTRUM : range of electromagnetic radiation with respect to its wavelength or frequency
1.4.1. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM
1.4.1.1. a spectrum of radiation that contains of all wavelength. no definite line that separate the colours. [RAINBOWS]
1.4.2. LINE SPECTRUM : a spectrum of radiation that consists of discrete lines of specific wavelength
1.4.2.1. EMISSION SPECTRUM
1.4.2.2. ABSORPTION SPECTRUM
1.4.3. HYDROGEN SPECTRUM
1.4.3.1. consists of discrete lines of specific (particular) wavelength. a line is form when an electron drops from a higher level to a lower level. the discrete line reflects that energy is quantized.
1.5. RYDBERG EQUATION
1.5.1. USED TO CALCULATE WAVELENGTH OF THE EMITTED PHOTON (any line) IN A GIVEN SERIES [1/λ = RZ2(1/n12 - 1/n22)]
1.6. IONIZATION ENERGY (IE)
1.6.1. MINIMUM ENERGY NEEDED FOR THE COMPLETE REMOVAL OF 1 MOL OF ELECTRON FROM 1 MOL OF GASEOUS ATMOS OR IONS [kj mol^-1]
