1. Includes
1.1. hair
1.2. skin
1.3. nails
1.4. glands
2. Functions
2.1. Temperate regulation
2.1.1. Controlling blood flow by skin and sweat glands
2.2. Protection
2.2.1. Acts as a physical barrier
2.3. Vitamin D production
2.3.1. exposure to uv light causes vitamin D synthesis
2.4. Excretion
2.4.1. loses waste products through skin and glands
2.5. Sensation
2.5.1. sensory receptors in skin
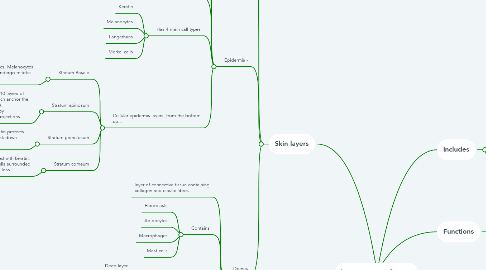
3. Skin layers
3.1. 2 parts
3.2. Epidermis -
3.2.1. Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
3.2.2. Cell produced by mitosis In basal layer and are pushed to the top
3.2.3. During this movement, cells change shape and chemical composition= keratinisation
3.2.4. Has 4 main call types
3.2.4.1. Keratin
3.2.4.2. Melanocytes
3.2.4.3. Langerhans
3.2.4.4. Merkel cells
3.2.5. Cellular epidermis layers: from the bottom up...
3.2.5.1. Stratum Basale
3.2.5.1.1. Stem cells, Merkel discs, Melanocytes, cuboidal cells which undergo mitotic division every 19 days.
3.2.5.2. Stratum spinosum
3.2.5.2.1. Melanocytes, keratinocytes. 8-10 layers of cells contain desmosomes which anchor the cells together. Contains keratin. Keratinocytes take in melanin by phagocytosis of melanocyte projections.
3.2.5.3. Stratum granulosum
3.2.5.3.1. 3-5 layers of flattened cells. Keratin protects and waterproofs. Cell nuclei break down leading to cell death.
3.2.5.4. Stratum corneum
3.2.5.4.1. 25+ layers of dead cells filled with keratin. Joined by desmosomes. Cells surrounded by lipids which prevent fluid loss.
3.3. Dermis
3.3.1. layer of connective tissue containing collagen and elastic fibres
3.3.2. Contains
3.3.2.1. Fibroblasts
3.3.2.2. Adipocytes
3.3.2.3. Macrophages
3.3.2.4. Mast cells
3.3.3. 2 layers:
3.3.3.1. Reticular
3.3.3.1.1. Deep layer
3.3.3.1.2. contains collegan and elastic fibres
3.3.3.1.3. spaces are occupied with hair follicles, nerves, oil glands, sweat glands, adipose
3.3.3.2. Papillary
3.3.3.2.1. superficial areolar connective tissue containing elastic fibres
3.3.3.2.2. Surface area increased by dermal papillae
4. Skin conditions
4.1. cyanosis
4.1.1. Lack of oxygen
4.1.2. skin turns blue
4.1.3. may result in heart failure
4.2. Jaundice
4.2.1. Yellowing of the skin
4.2.2. Due to build up of bile pigment called bilirubin
4.3. Erythema
4.3.1. Redenning of the skin
4.3.2. enlargment of capillaires
4.4. Pallor
4.4.1. Loss of colour
4.4.2. Decreased blood supply
5. Hair composition
5.1. 3 layers:
5.1.1. Medulla
5.1.1.1. 2-3 layers of irregular shaped cells. Where hair is formed
5.1.2. Cortex
5.1.2.1. major part of shaft
5.1.3. Cuticle
5.1.3.1. single layer of highly keratinised thin flat cells holding hair in follicle. At base of each follicle is the bulb. The bulb houses the papilla- connective tissue and blood vessels.
6. Glands
6.1. Sebaceous gland
6.1.1. Oil glands mostly connected to hair follicle
6.1.2. secretes sebum
6.1.3. prevents hair from drying
6.2. Sudoriferous gland
6.2.1. 2 types
6.2.1.1. eccrine
6.2.1.1.1. secretion onto skins surface
6.2.1.1.2. extend through dermis and epidermis
6.2.1.2. apocrine
6.2.1.2.1. secretes into hair follicle
6.2.1.2.2. located in dermis or hypodermis and opens in hair follicle
6.3. Ceruminous gland
6.3.1. sweat glands in ear
6.3.2. produce waxy secretions
