Detection Cancer
by ฮาซิม สาแม
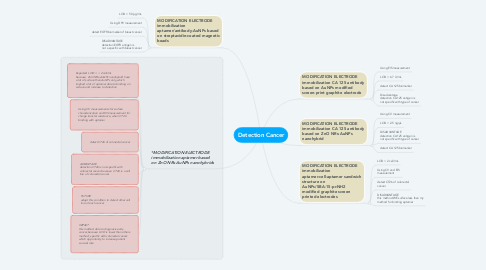
1. MODIFICATION ELECTRODE immobilization CA 125 antibody based on AuNPs modified screen-print graphite electrode
1.1. Using EIS measurement
1.2. LOD = 6.7 U/mL
1.3. detect CA 125 biomarker
1.4. Disadvantage detection CA 125 antigen is not specific with type of cancer
2. MODIFICATION ELECTRODE immobilization CA 125 antibody based on ZnO NRs-AuNPs nanohybrid
2.1. Using CV measurement
2.2. LOD = 2.5 ng/μL
2.3. DISADVANTAGE detection CA 125 antigen is not specific with type of cancer
2.4. detect CA 125 biomarker
3. MODIFICATION ELECTRODE immobilization aptamer-cell-aptamer sandwich structure on AuNPs/SBA-15-pr-NH2 modified graphite screen printed electrodes
3.1. LOD = 2 cell/mL
3.2. Using CV and EIS measurement
3.3. detect CT26 of colorectal cancer
3.4. DISADVANTAGE this method WE surface less than my method for binding aptamer
4. MODIFICATION ELECTRODE immobilization aptamer/antibody-AuNPs based on streptavidin-coated magnetic beads
4.1. LOD = 50 pg/mL
4.2. Using DPV measurement
4.3. detect EGFR biomarker of breast cancer
4.4. DISADVANTAGE detection EGFR antigen is not a specific with breast cancer
5. *MODIFICATION ELECTRODE immobilization aptamer based on ZnO NRs-AuNPs nanohybrids
5.1. Expected LOD = < 2 cell/mL because ZnO NRs-AuNPs nanohybrid have a lot of surface than AuNPs only, which implied a lot of aptamer able to binding on surface and increase to detection
5.2. Using CV measurements for surface characterization and EIS measurement for charge transfer resistance, when CT 26 binding with aptamer
5.3. detect CT26 of colorectal cancer
5.4. ADVANTAGE detection CT26 is not specific with colorectal cancer because CT 26 is a cell line of colorectal cancer
5.5. FUTURE adapt this condition to detect other cell line of each cancer
5.6. IMPACT this method able to diagnosis early cancer,because LOD is lower than others method, specific with colorectal cancer. which opportunity to increase patient survival rate


