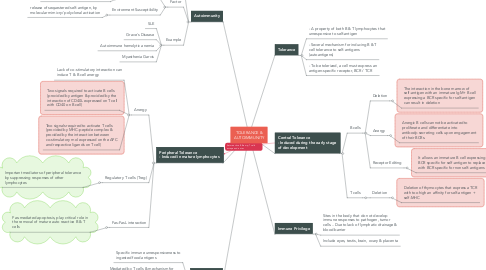
1. Tolerance
1.1. - A property of both B & T lymphocytes that unresponsive to self-antigen
1.2. - Several mechanism for inducing B & T cell tolerance to self-antigens (autoantigens)
1.3. - To be tolerized, a cell must express an antigen-specific receptor, BCR / TCR
2. Autoimmunity
2.1. Definition - body mounts an immune response to one/more self-antigen
2.2. Factor
2.2.1. Genetic Susceptibility
2.2.1.1. Alleles of the major histocompatibility complex (HLA)
2.2.2. Environment Susceptibility
2.2.2.1. release of sequestered self-antigen, by molecular mimicry/ polyclonal activation
2.3. Example
2.3.1. SLE
2.3.2. Grave's Disease
2.3.3. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
2.3.4. Myasthenia Garvis
3. Central Tolerance - Induced during the early stage of development
3.1. B cells
3.1.1. Deletion
3.1.1.1. The interaction in the bone marrow of self-antigen with an immature IgM+ B cell expressing a BCR specific for self-antigen can result in deletion
3.1.2. Anergy
3.1.2.1. Anergic B cells cannot be activated to proliferate and differentiate into antibody-secreting cells upon engagement of their BCRs.
3.1.3. Receptor Editing
3.1.3.1. It allows an immature B cell expressing a BCR specific for self-antigen to replace it with BCR specific for non self-antigens
3.2. T cells
3.2.1. Deletion
3.2.1.1. Deletion of thymocytes that express a TCR with too high an affinity for self-antigen + self-MHC
4. Peripheral Tolerance - Induced in mature lymphocytes
4.1. Anergy
4.1.1. Lack of co-stimulatory interaction can induce T & B cell anergy
4.1.2. Two signals required to activate B cells (provided by antigen & provided by the interaction of CD40L expressed on T cell with CD40 on B cell)
4.1.3. Two signals required to activate T cells (provided by MHC-peptide complex & provided by the interaction between co-stimulatory mol expressed on the APC and respective ligands on T cell)
4.2. Regulatory T cells (Treg)
4.2.1. Important mediators of peripheral tolerance by suppressing responses of other lymphocytes
4.3. Fas-FasL interaction
4.3.1. Fas-mediated apoptosis, play critical role in the removal of mature auto reactive B & T cells

