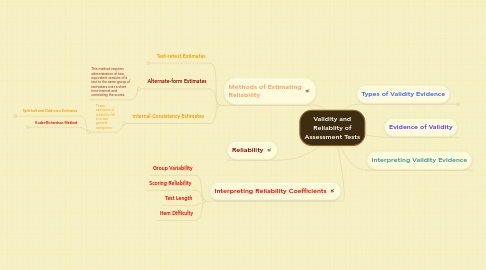
1. Reliability
2. Methods of Estimating Reliability
2.1. Test-retest Estimates
2.1.1. This method requires administration of the same test twice over a pre-determined time interval to the same group of test-takers.
2.2. Alternate-form Estimates
2.2.1. This method requires administration of two equivalent versions of a test to the same group of test-takers over a short time-interval and correlating the scores.
2.3. Internal Consistency Estimates
2.3.1. These estimates of reliability fall into two general categories:
2.3.1.1. Split-half and Odd-even Estimates
2.3.1.1.1. These estimates involve dividing a test into halves and correlating them with one another.
2.3.1.2. Kuder-Richardson Method
2.3.1.2.1. Kuder-Richardson methods are used to determine how much the entire test can consistently mearsure a concept.
3. Interpreting Reliability Coefficients
3.1. Group Variability
3.2. Scoring Reliability
3.3. Test Length
3.4. Item Difficulty
4. Types of Validity Evidence
4.1. Construct Validity Evidence
4.2. Criterion-Related Validity Evidence
4.2.1. Concurrent Criterion-Related Validity Evidence
4.2.2. Predictive Criterion-Related Validity Evidence
