Types of Stabilisation
by Leah Fisher
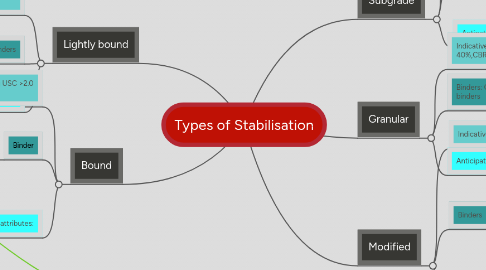

1. Lightly bound
1.1. Indicative strength after stabilisation USC 1.0 - 2.0 MPa
1.2. Binders
1.2.1. Cementitious binders
1.2.2. Lime
1.3. Anticipated performance attributes
1.3.1. Similar to Modified
2. Bound
2.1. Indicative strength after stabilising USC >2.0 MPa
2.2. Binder
2.2.1. Greater quantities of Cementitious binder
2.2.2. Combination of cementitious and bituminous binder
2.3. Anticipated performance attributes:
2.3.1. Increased pavement stiffness to provide tensile resistance
2.3.2. Greatest stiffness and hence load carrying capacity
3. Subgrade
3.1. Indicative strength after stabilising >5%
3.2. Binders: Addition of lime and chemical binders
3.3. Antipated performance attributes:
3.3.1. Improved subgrade stiffness
3.3.2. Improved shear strength
3.3.3. Reduced heave and shringake
4. Granular
4.1. Indicative strength after stabilising 40%,CBR<70% subbase and base course
4.2. Binders: Other granular materials classified as binders
4.3. Anticipated performance attributes:
4.3.1. Improved pavement stiffness
4.3.2. Improved shear strength
4.3.3. Improved resistance to aggregate breakdown
5. Modified
5.1. Indicative strength after stabilisation: 0.7MPa<UCS<1.0MPa
5.2. Binders
5.2.1. Cementitious binders
5.2.2. Lime
5.2.3. Chemical
5.2.4. Combination
5.3. Anticipated performance attributes:
5.3.1. Improved pavement stiffness
5.3.2. Improved shear strength
5.3.3. Reduced moisture sensitivity
