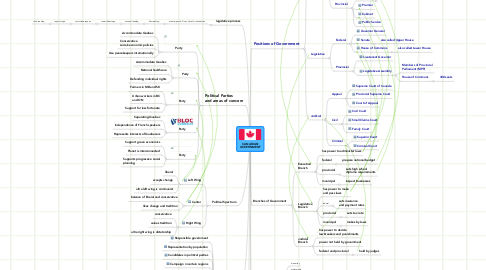
1. Political Parties and areas of concern
1.1. Party
1.1.1. Accommodate Quebec
1.1.2. Conservative social+economic policies
1.1.3. Use peacekeepers internationally
1.2. Party
1.2.1. Accommodate Quebec
1.2.2. National healthcare
1.2.3. Defending individual rights
1.3. Party
1.3.1. Farmers in MB and SK
1.3.2. Urban workers in BC and ON
1.3.3. Support for less fortunate
1.4. Party
1.4.1. Separating Quebec
1.4.2. Independence of French speakers
1.4.3. Represents interests of Quebecers
1.5. Party
1.5.1. Support green economics
1.5.2. Planet is interconnected
1.5.3. Supports progressive social planning
2. Political Spectrum
2.1. Left Wing
2.1.1. liberal
2.1.2. accepts change
2.1.3. ultra left wing is communist
2.2. Center
2.2.1. balance of liberal and conservative
2.2.2. likes change and tradition
2.3. Right Wing
2.3.1. conservative
2.3.2. values tradition
2.3.3. ultra right wing is dictatorship
3. Electoral System
3.1. Responsible government
3.2. Representation by population
3.3. Candidates in political parties
3.4. Campaign in certain regions
3.5. Representatives chosen by First Past the Post
3.6. Party with most seats becomes party in charge
3.7. Parliament can be majority, minority or coalition
3.8. Parliament dissolves and electoral system restarts
4. legislative process
4.1. minister puts bill on notice for intruduction
4.1.1. first reading
4.1.1.1. second reading
4.1.1.1.1. committee stage
5. government structure
5.1. the public
5.1.1. voters
5.1.1.1. elected assembly
5.1.1.1.1. legislative
5.1.1.1.2. executive
6. Positions of Government
6.1. Executive
6.1.1. Federal
6.1.1.1. Queen
6.1.1.1.1. represented by Governor General
6.1.1.2. Prime Minister
6.1.1.3. Cabinet
6.1.1.4. Public Service
6.1.2. Provincial
6.1.2.1. Queen
6.1.2.1.1. represented by Lieutenant Governor
6.1.2.2. Premier
6.1.2.3. Cabinet
6.1.2.4. Public Service
6.2. Legislative
6.2.1. Federal
6.2.1.1. Governor General
6.2.1.2. Senate
6.2.1.2.1. also called Upper House
6.2.1.3. House of Commons
6.2.1.3.1. also called Lower House
6.2.2. Provincial
6.2.2.1. Lieutenant Governor
6.2.2.2. Legislative Assembly
6.2.2.2.1. Members of Provincial Parliament (MPP)
6.2.2.2.2. House of Commons
6.3. Judicial
6.3.1. Appeal
6.3.1.1. Supreme Court of Canada
6.3.1.2. Provincial Supreme Court
6.3.1.3. Court of Appeal
6.3.2. Civil
6.3.2.1. Civil Court
6.3.2.2. Small Claims Court
6.3.2.3. Family Court
6.3.3. Criminal
6.3.3.1. Superior Court
6.3.3.2. Criminal Court
7. Branches of Government
7.1. Executive Branch
7.1.1. has power to administer laws
7.1.2. federal
7.1.2.1. prepare national budget
7.1.3. provincial
7.1.3.1. sets high school diploma requirements
7.1.4. municipal
7.1.4.1. inspect businesses
7.2. Legislative Branch
7.2.1. has power to make and pass laws
7.2.2. federal
7.2.2.1. sets insurance and payment rates
7.2.3. provincial
7.2.3.1. sets tax rate
7.2.4. municipal
7.2.4.1. makes by-laws
7.3. Judicial Branch
7.3.1. has power to decide lawbreakers and punishments
7.3.2. power not held by government
7.3.3. federal and provincial
7.3.3.1. held by judges
8. types of government
8.1. monarchy
8.2. dictatorship
8.3. democracy
8.4. republic
8.5. communism
8.6. constitutional monarchy
8.6.1. this is our government
