Rational Functions
by Mar’a Isabel Chac—n Moscoso
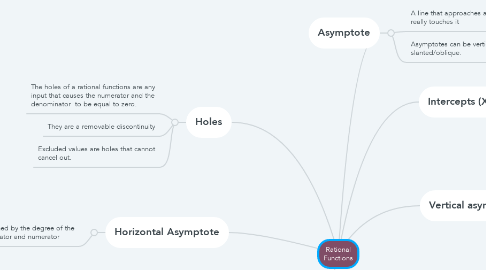

1. Holes
1.1. The holes of a rational functions are any input that causes the numerator and the denominator to be equal to zero.
1.2. They are a removable discontinuity
1.3. Excluded values are holes that cannot cancel out.
2. Horizontal Asymptote
2.1. Determined by the degree of the denominator and numerator
2.1.1. When the degree of the denominator is bigger than the degree of the numerator y=0.
2.1.2. When the degree of the denominator is equal to the degree of the numerator y=a value
3. Slanted Asymptotes
3.1. A slanted asymptote happens when the numerator is greater that the denominator by one. (Quotient numerator/denominator)
4. Asymptote
4.1. A line that approaches a curve but never really touches it
4.2. Asymptotes can be vertical, horizontal or slanted/oblique.
5. Intercepts (X and Y)
5.1. The x-intercepts are where the graph crosses the x-axis, and the y-intercepts are where the graph crosses the y-axis.
5.1.1. To find the x-intercept plug in 0 in y. The x-intercept are zeros of the denominator that are not repeated in the numerator.
5.1.1.1. To find the y-intercept plug in 0 in x and solve for y. The y-intercepts are the point in the graph where the line crosses the y-axis.
6. Vertical asymptotes
6.1. They are found using the zeros in the denominator of a rational function.
6.1.1. Vertical straight line that goes to infinity.
