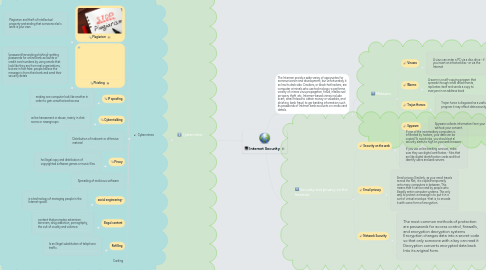
1. Сybercrime
1.1. Cybercrimes
1.1.1. Plagiarism
1.1.1.1. Plagiarism and theft of intellectual property-pretending that someone else's work is your own
1.1.2. Phishing
1.1.2.1. (password harvesting phishing)-getting passwords for online bank accounts or credit card numbers by using emails that look like they are from real organizations, but are in fact fake: people belleve the message is from their bank and send their security detals
1.1.3. IP spoofing
1.1.3.1. making one computer look like another in order to gain unauthorized access
1.1.4. Cyberstalking
1.1.4.1. online harassment or abuse, mainiy in chat rooms or newsgroups
1.1.5. Distribution of indecent or offensive material
1.1.6. Piracy
1.1.6.1. he illegal copy and distribution of copyrighted software games or music files
1.1.7. Spreading of malicious software
1.1.8. social engineering-
1.1.8.1. is a technology of managing people in the Internet space.
1.1.9. Illegal content
1.1.9.1. content that promotes extremism, terrorism, drug addiction, pornography, the cult of cruelty and violence.
1.1.10. Refilling
1.1.10.1. Іs an illegal substitution of telephone traffic.
1.1.11. Carding
2. The Intermer proids a wide varieу of opporuntes for кommunicarion and development, bur unfortunately it so has its dark side. Crackers, or black-hat hackers, are computer criminals who use technolоgy го рerforma variety of crimes virus propagation, fraud, intellecrual prгopery theft, etc. Intermer-based crimes include scam, email fraаиd to obtain money or valuables, and phishing, bank fraud, to ger banking information such as passwords of Interner bank accounts or cтedix card details.
2.1. Malware:
2.1.1. Viruses
2.1.1.1. A virus can enter a PC via a disc drive - if you insert an infected disc -or via the Internet
2.1.2. Worms
2.1.2.1. A worm is a self-copying progam that spreads through email attachments, replicates itself and sends a copy to everyone in an address book
2.1.3. Trojan Horses
2.1.3.1. Trojan horse is disguised as a useful program it may affect data security
2.1.4. Spyware
2.1.4.1. Spyware collects information from your PC without your consent.
3. Security and privacy on the Internet.
3.1. Security on the web
3.1.1. If one of the intermediary computers is infiltrated by hackers, your data can be copied To avoid risks, you should set al security alerts to high on your web browser. If you use online banking services, make sure they use digital certificates - files that are like digital identification cards and that identify users and web servers
3.2. Email privacy
3.2.1. Email privacy Similarly, as your email travels across the Net, it is copled temporarily onto many computers in between. This means that it can be read by people who illegally enter computer systems. The only way to protect a message is to put it in a sort of virtual envelope -that is, to encode it with some form of encryption.
3.3. Network Sucurity
3.3.1. The most common methods of protection are passwords for access control, firewalls, and encryption decryption systems Encryption changes data into a secret code so that only someone with a key can read it Decryption converts encrypted data back Into its ariginal form.
