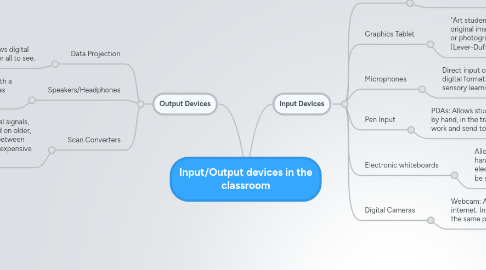
1. Input Devices
1.1. Scanners
1.1.1. Flatbed Scanner: Uploading images from a hard source to a digital format
1.2. Graphics Tablet
1.2.1. "Art students can use a more typical digitizer to draw original images, enhance computer-generated images or photographs, or annotate scanned images" (Lever-Duffy & McDonald, 2011, p. 151).
1.3. Microphones
1.3.1. Direct input of spoken word or other audio into digital format. Allows combining different sensory learning styles into one project.
1.4. Pen Input
1.4.1. PDAs: Allows students to work math products by hand, in the traditional way, and save their work and send to the instructor electronically.
1.5. Electronic whiteboards
1.5.1. Allows the user to instantly save all hand-written notes, drawings, etc. in an electronic format. The notes could then be sent to all learners.
1.6. Digital Cameras
1.6.1. Webcam: Allows teleconferencing using the internet. Instructors and learners need not be in the same physical location.
2. Output Devices
2.1. Data Projection
2.1.1. Replaces overhead projectors. Allows digital imagesto be projected in an area for all to see.
2.2. Speakers/Headphones
2.2.1. Allows for audio information to be shared with a group, as with speakers, or with individuals, as with headphones.
2.3. Scan Converters
2.3.1. Analog TV converters: Allows digital signals, such as a PC signal, to be displayed on older, analog televisions. A good bridge between older/newer technologies that is inexpensive (Lever-Duffy & McDonald, 2001).
