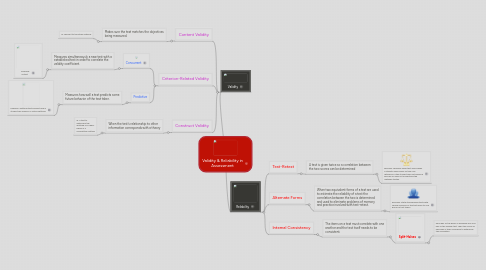
1. Validity
1.1. Content Validity
1.1.1. Makes sure the test matches the objectives being measured.
1.1.1.1. Ie: relevant to the study material
1.2. Criterion-Related Validity
1.2.1. Concurrent
1.2.1.1. Measures simultaneously a new test with a established test in order to correlate the validity coefficient.
1.2.1.1.1. Example: IQ test
1.2.2. Predictive
1.2.2.1. Measures how well a test predicts some future behavior of the test taker.
1.2.2.1.1. Example: Aptitude tests predict how a student will preform in future settings
1.3. Construct Validity
1.3.1. When the test's relationship to other information corresponds with a theory
1.3.1.1. Ie: A test to determine the aptitude of a chess player in a competition setting
2. Reliability
2.1. Test-Retest
2.1.1. A test is given twice so a correlation between the two scores can be determined
2.1.1.1. Example: Teachers allow test-overs when a studetn does poorly so they can determine if the student was jsut having a bad day or does not understand the materials tested.
2.2. Alternate Forms
2.2.1. When two equivalent forms of a test are used to estimate the reliability of a test the correlation between the two is determined and used to eliminate problems of memory and practice involved with test-retest.
2.2.1.1. Example: State standardized tests with several versions of the test given to one group of test takers
2.3. Internal Consistency
2.3.1. The items on a test must correlate with one another and the test itself needs to be consistent.
2.3.1.1. Split-Halves
2.3.1.1.1. Each half of the group is assigned only one half of the original test. Then the scores of each half is then compared to determine the correlation.
