Structure of Matter
by Elizabeth Grimm
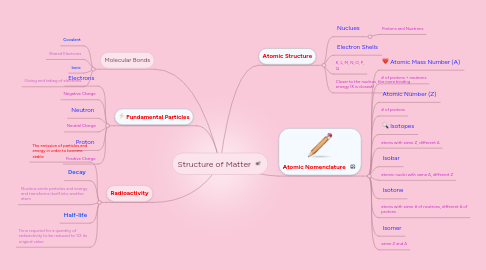

1. Fundamental Particles
1.1. Electrons
1.2. Negative Charge
1.3. Neutron
1.4. Neutral Charge
1.5. Proton
1.6. Positive Charge
2. Radioactivity
2.1. The emission of particles and energy in order to become stable
2.2. Decay
2.3. Nucleus emits particles and energy and transforms itself into another atom
2.4. Half-life
2.5. Time required for a quantity of radioactivity to be reduced to 1/2 its original value
3. Molecular Bonds
3.1. Covalent
3.2. Shared Electrons
3.3. Ionic
3.4. Giving and taking of electrons
4. Atomic Nomenclature
4.1. Atomic Mass Number (A)
4.2. # of protons + neutrons
4.3. Atomic Number (Z)
4.4. # of protons
4.5. Isotopes
4.6. atoms with same Z, different A
4.7. Isobar
4.8. atomic nuclei with same A, different Z
4.9. Isotone
4.10. atoms with same # of neutrons, different # of protons
4.11. Isomer
4.12. same Z and A
5. Atomic Structure
5.1. Nuclues
5.1.1. Protons and Nuetrons
