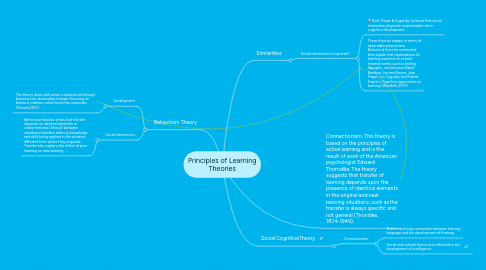
1. Behavirism Theory
1.1. Development
1.1.1. The theory deals with what is understood through behaviors on observable changes focusing on behavior patterns which becomes automatic (Schunk,2012).
1.2. Social Interactions
1.2.1. Behavioral theories stress that transfer depends on identical elements or similar features (Stimuli) between situations transfers refers to knowledge and skills being applied in the situation different from where they acquired. Transfer also explains the effect of prior learning on new learning.
2. Social CognitiveTheory
2.1. Connectionism
2.1.1. There is a strong connection between learning language and the development of thinking.
2.1.2. Social and cultural factors are influential in the development of intelligence.
3. Similarities
3.1. Social interaction is important!
3.1.1. Both Piaget & Vygotsky believed that social interaction played an irreplaceable role in cognitive development.
3.1.2. These theories explain in terms of observable phenomena. Behavioral theories contended that explain that explanations for learning need not to include internal events such as feeling, thoughts, not because Albert Bandura, Jerome Bruner, Jean Piaget, Lev Vygosky and Robert Gagne's Cognitive approaches to learning (Woolfolk, 2010)
