Self-Determination Theory
by Sean Todd
1. Diagram of progression from amotivation to intrinsic motivation (from top to bottom)
1.1. Amotivation
1.2. External Regulation
1.3. Introjected Regulation
1.4. Identified Regulation
1.5. Intrinsic Motivation
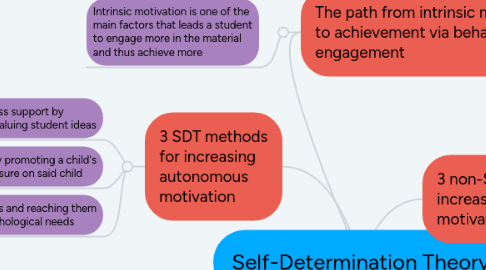
2. 3 SDT methods for increasing autonomous motivation
2.1. Teacher autonomy-relatedness support by praising students often and valuing student ideas
2.2. Parent autonomy-relatedness support by promoting a child's independence and exerting minimal pressure on said child
2.3. Developing intrinsic life goals and reaching them which fulfill a student's psychological needs
3. The path from intrinsic motivation to achievement via behavioral engagement
3.1. Intrinsic motivation is one of the main factors that leads a student to engage more in the material and thus achieve more
4. Three universal psychological needs
4.1. Relatedness
4.2. Competence
4.3. Autonomy
5. 3 non-SDT methods for increasing autonomous motivation
5.1. Learning goals are what students should be able to do achieve a certain lesson
5.2. Mastery goals are students aiming for a certain level of competence in a certain field
5.3. Having a growth mindset and believing that hard work and dedication will help with self-improvement


