Theoretical Perspectives
作者:Beverly Combes
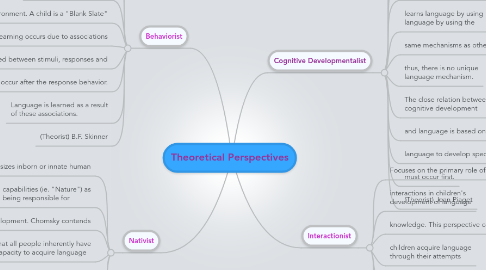
1. Behaviorist
1.1. Emphasizes the role of "Nurture" and
1.2. Considers learning to occur based on the
1.3. stimuli, responses, and reinforcements that occur
1.4. in the environment. A child is a "Blank Slate"
1.5. and learning occurs due to associations
1.6. established between stimuli, responses and
1.7. events that occur after the response behavior.
1.8. Language is learned as a result of these associations.
1.9. (Theorist) B.F. Skinner
2. Nativist
2.1. Emphasizes inborn or innate human
2.2. capabilities (ie. "Nature") as being responsible for
2.3. Language development. Chomsky contends
2.4. that all people inherently have capacity to acquire language
2.5. due to cognitive structures that process language differently from other stimuli.
2.6. (Theorist) Noam Chomsky
3. Cognitive Developmentalist
3.1. Emphasis of this perspective is that
3.2. language is acquired as maturation
3.3. occurs and cognitive competencies develop.
3.4. this perspective also proposes that a child
3.5. learns language by using language by using the
3.6. same mechanisms as other learning.
3.7. thus, there is no unique language mechanism.
3.8. The close relation between cognitive development
3.9. and language is based on the belief that for
3.10. language to develop specific cognitive growth
3.11. must occur first.
3.12. (Theorist) Jean Piaget
4. Interactionist
4.1. Focuses on the primary role of sociocultural
4.2. interactions in children's development of language
4.3. knowledge. This perspective contends that
4.4. children acquire language through their attempts
4.5. to communicate with the world around them.
4.6. (Theorists) Vygotsky, Bruner, Halliday


