money and interest rates
by Linh Khánh
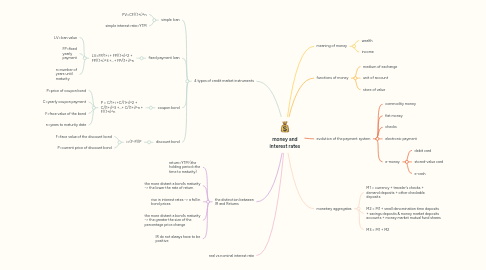

1. 4 types of credit market instruments
1.1. simple loan
1.1.1. PV=CF/(1+i)^n
1.1.2. simple interest rate=YTM
1.2. fixed payment loan
1.2.1. LV=FP/1+i + FP/(1+i)^2 + FP/(1+i)^3 +...+ FP/(1+i)^n
1.2.1.1. LV=loan value
1.2.1.2. FP=fixed yearly payment
1.2.1.3. n=number of years until maturity
1.3. coupon bond
1.3.1. P = C/1+i +C/(1+i)^2 + C/(1+i)^3 +...+ C/(1+i)^n + F/(1+i)^n
1.3.1.1. P=price of coupon bond
1.3.1.2. C=yearly coupon payment
1.3.1.3. F=face value of the bond
1.3.1.4. n=years to maturity date
1.4. discount bond
1.4.1. i=(F-P)/P
1.4.1.1. F=face value of the discount bond
1.4.1.2. P=current price of discount bond
2. the distinction between IR and Returns
2.1. return=YTM (the holding period=the time to maturity)
2.2. the more distant a bond’s maturity -> the lower the rate of return
2.3. rise in interest rates -> a fall in bond prices
2.4. the more distant a bond’s maturity -> the greater the size of the percentage price change
2.5. IR do not always have to be positive
3. real vs nominal interest rate
4. meaning of money
4.1. wealth
4.2. income
5. functions of money
5.1. medium of exchange
5.2. unit of account
5.3. store of value
6. evolution of the payment system
6.1. commodity money
6.2. fiat money
6.3. checks
6.4. electronic payment
6.5. e-money
6.5.1. debit card
6.5.2. stored-value card
6.5.3. e-cash
