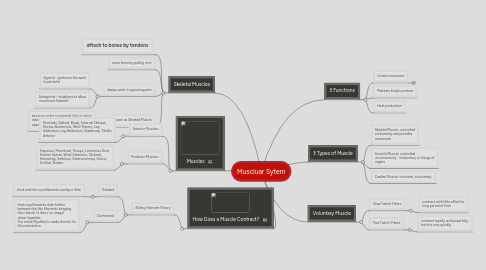
1. Skeletal Muscles
1.1. attach to bones by tendons
1.2. move bone by pulling on it
1.3. always work in opposing pairs
1.3.1. Agonist - performs the work (contracts)
1.3.2. Antagonist - lengthens to allow movement (relaxes)
1.4. Known as Striated Muscle
1.4.1. because under a polarised light or when stained with indicator, it has a striped appearance.
2. Muscles
2.1. Anterior Muscles:
2.1.1. Pectorals, Deltoid, Bicep, External Oblique, Rectus Abdominus, Wrist Flexors, Leg Adductors, Leg Abductors, Quadricep, Tibialis Anterior
2.2. Posterior Muscles:
2.2.1. Trapezius, Rhomboid, Triceps, Latissimus Dorsi, Erector Spinae, Wrist Extensors, Gluteals, Hamstring, Sartorius, Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Achilles Tendon
3. How Does a Muscle Contract?
3.1. Sliding Filament Theory
3.1.1. Relaxed
3.1.1.1. thick and thin myofilaments overlap a little.
3.1.2. Contracted
3.1.2.1. thick myofilaments slide further between the thin filaments bringing the z bands ('z discs' on image) closer together. The entire Myofibril is made shorter for the contraction.
4. 3 Functions
4.1. Create movement
4.1.1. Sub Idea 1
4.1.2. Sub Idea 2
4.2. Maintain body's posture
4.3. Heat production
5. 3 Types of Muscle
5.1. Skeletal Muscle: controlled vonluntarily and provides movement
5.2. Smooth Muscle: controlled unconsciously - involuntary. in linings of organs
5.3. Cardiac Muscle: the heart, involuntary.
6. Voluntary Muscle
6.1. Slow Twitch Fibres
6.1.1. contract with little effort for long period of time
6.2. Fast Twitch Fibres
6.2.1. contract rapidly and powerfully, but tire very quickly
