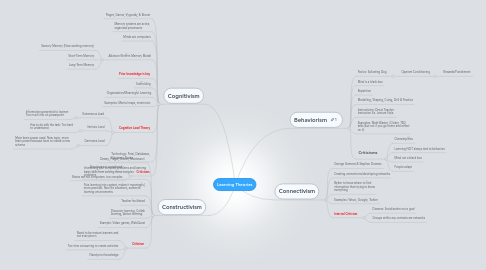
1. Cognitivism
1.1. Piaget, Garner, Vygostky, & Bruner
1.2. Memory systems are active, organized processors
1.3. Minds are computers
1.4. Atkinson-Shriffrin Memory Model
1.4.1. Sensory Memory (Now working memory)
1.4.2. Short-Term Memory
1.4.3. Long-Term Memory
1.5. Prior knowledge is key
1.6. Scaffolding
1.7. Organization/Meaningful Learning
1.8. Examples: Mental maps, mnemonic
1.9. Cognitive Load Theory
1.9.1. Extraneous Load
1.9.1.1. Information presented to learner: Too much info on powerpoint
1.9.2. Intrinsic Load
1.9.2.1. Has to do with the task: Too hard to understand
1.9.3. Germaine Load
1.9.3.1. More brain power used: New topic, more brain power because have to create a new schema
1.10. Technology: Prezi, Databases, Electronic Notes
1.11. Criticisms
1.11.1. Emotions not considered
1.11.2. Brains are not computers: too complex
2. Constructivism
2.1. Dewey, Piaget, Bruner, Montessori
2.2. Interacting with complex problems and learning basic skills from solving these complex problems
2.3. Puts learning into context, makes it meaningful, more practical. Real life situations, authentic learning environments
2.4. Teacher facilitated
2.5. Discovery learning, Collab learning, Active learning
2.6. Example: Video games, WebQuest
2.7. Criticism
2.7.1. Need to be mature learners and not everyone is
2.7.2. Too time consuming to create activities
2.7.3. Need prior knowledge
3. Behaviorism
3.1. Pavlov: Salivating Dog
3.1.1. Operant Conditioning
3.1.1.1. Rewards/Punishment
3.2. Mind is a black box
3.3. Repetition
3.4. Modelling, Shaping, Cuing, Drill & Practice
3.5. Instructivism: Direct Teacher Instruction Ex. Lecture Style.
3.6. Examples: Math Blaster, iClicker, TED talks (but not if you go home and reflect on it)
3.7. Criticisms
3.7.1. Oversimplifies
3.7.2. Learning NOT always tied to behaviors
3.7.3. Mind not a black box
3.7.4. People adapt
4. Connectivism
4.1. George Siemens & Stephen Downes
4.2. Creating connections/developing networks
4.3. Better to know where to find information than trying to know everything
4.4. Examples: Yahoo, Google, Twitter
4.5. Internal Criticism
4.5.1. Downes: Socialization not a goal
4.5.2. Groups within any contexts are networks
