21st century skills
by marielli bautista
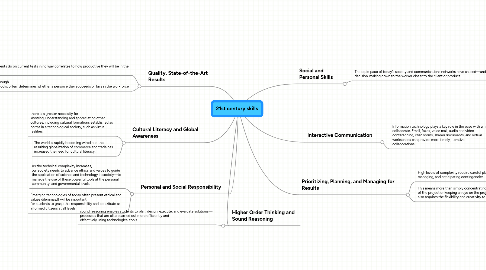
1. Quality, State-of-the-Art Results
1.1. Levin concluded that how well students do on current tests in no way correlates to how productive they will be in the workforce.
1.2. High productivity, on the other hand, though currently not a high stakes focus of schools, often determines whether a person either succeeds or fails in the workforce.
2. Personal and Social Responsibility
2.1. As the technical complexity increases, our society needs to advance ethics and values to guide the application of science and technology in society—to manage the use of these powerful tools at the personal, community, and governmental levels.
2.2. Emerging technologies of today often present ethical and values dilemmas.It will be important for students to grasp this responsibility and contribute as informed citizens at all levels.
3. Cultural Literacy and Global Awareness
3.1. there is a greater necessity for knowing, understanding and appreciating other cultures, including cultural formations established as norms in a technological society, such as virtual realities.
3.2. The world is rapidly becoming wired and the resulting globalization of commerce and trade has increased the need for cultural literacy.
4. Higher Order Thinking and Sound Reasoning
4.1. sound reasoning enables students to plan, design, execute, and evaluate solutions— processes that are often carried out more efficiently and effectively using technological tools.
5. Social and Personal Skills
5.1. The rapid pace of today’s society and communications networks have caused—and enabled—a shift in the level of decision-making down to the worker closer to the client or product.
6. Prioritizing, Planning, and Managing for Results
6.1. High levels of complexity require careful planning, managing, and anticipating contingencies
6.2. This means more than simply concentrating on reaching the main goals of the project or keeping an eye on the project outcomes. It also requires the flexibility and creativity to anticipate unexpected outcomes as well.
7. Interactive Communication
7.1. Information technology plays a key role in the ease with which individuals and groups collaborate. Email, faxes, voice mail, audio and video conferencing, chat rooms, shared documents, and virtual workspaces can provide more timely, iterative collaborations.


