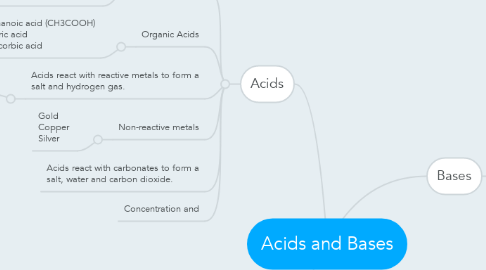
1. Acids
1.1. Mineral Acids
1.1.1. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) Nitric acid (HNO3) Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) Phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
1.2. Organic Acids
1.2.1. Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) Citric acid Ascorbic acid
1.3. Acids react with reactive metals to form a salt and hydrogen gas.
1.3.1. Reactive metals
1.3.1.1. Magnesium Sodium
1.4. Non-reactive metals
1.4.1. Gold Copper Silver
1.5. Acids react with carbonates to form a salt, water and carbon dioxide.
1.6. Concentration and
2. Bases
2.1. Properties of Acid
2.1.1. Have a soapy taste
2.1.2. Conduct electricity when dissolved in water
2.1.3. Slippery feeling
2.2. Uses of Base
2.2.1. Bases
2.2.1.1. Sodium hydroxide
2.2.1.1.1. Make soap and detergents
2.2.1.2. Aqueous ammonia
2.2.1.2.1. Make fertilizers
2.2.1.3. Magnesium hydroxide
2.2.1.3.1. Used in toothpaste
2.3. Concentration and Strength
2.3.1. Concentration - Adding more of the base in it
2.3.2. Strength - High concentration of hydroxide ions in it
2.4. Definition and Types
2.4.1. A base is any metal oxide or metal hydroxide.
2.4.2. Alkalis react with ammonium salts to form a salt, water and ammonia gas.
2.5. pH scales and indicator
2.5.1. pH value of above 7
2.5.2. Turn red litmus paper red
2.5.3. Turn universal indicator blue or violet
2.5.4. Turn methyl orange yellow
3. Importance of pH
3.1. Crops and plants
3.1.1. Crops and plants will die when the soil is too acidic or akaline
3.2. Marine Animals
3.2.1. Die due to too much acidity from acid rain
