Dalton's Model of Matter
by Rafael Muñoa
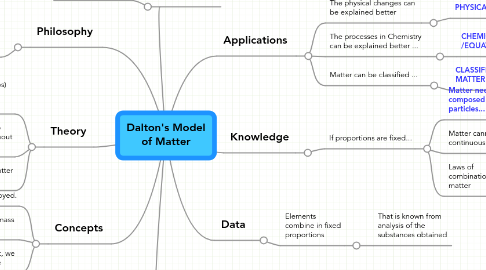

1. Events Observed
1.1. Ratios in combination of elements
2. Focus Question
2.1. Is Matter continuous or discontinuous?
3. Concepts
3.1. Matter is not created nor destroyed.
3.2. In a chemical reaction the total mass remains constant
3.3. By measuring the mass of each component, we can control the ratio in which they combine
4. Theory
4.1. From macroscopic measures (mass, ratios) we can reach conclusions about the microscopic world (how matter is made)
4.2. Combination of elements at any ratio means that matter is continuous, without small units.
4.3. Combination at fixed ratios means that matter is discontinuous, made of smaller units.
5. Philosophy
5.1. The knowledge of the structure of matter can help explain the nature and improve our lives.
6. Data
6.1. Elements combine in fixed proportions
6.1.1. That is known from analysis of the substances obtained
7. Knowledge
7.1. If proportions are fixed...
7.1.1. Matter need to be composed of discrete particles...
7.1.1.1. ...called atoms
7.1.1.1.1. From here...
7.1.2. Matter cannot be continuous
7.1.2.1. Matter is discontinuous
7.1.3. Laws of combination of matter
8. Applications
8.1. The physical changes can be explained better
8.1.1. PHYSICAL CHANGES
8.2. The processes in Chemistry can be explained better ...
8.2.1. CHEMICAL REACTIONS /EQUATIONS
8.3. Matter can be classified ...
8.3.1. CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER
