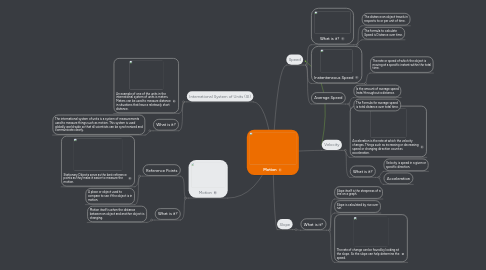
1. International System of Units (SI)
1.1. An example of one of the units in the international system of units is meters. Meters can be used to measure distance in situations that have a reletavely short distance.
1.2. What is it?
1.2.1. The international system of units is a system of measurements used to measure things such as motion. This system is used globally world wide so that all scientists can be synchronized and communicate clearly.
2. Motion
2.1. Reference Points
2.1.1. Stationary Objects serve as the best reference points as they make it easier to measure the motion.
2.1.2. A place or object used to compare to see if the object is in motion.
2.2. What is it?
2.2.1. Motion itself is when the distance between an object and another object is changing.
3. Velocity
3.1. Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity changes. Things such as increasing or decreasing speed or changing direction count as acceleration.
3.2. What is it?
3.2.1. Velocity is speed in a given or specific direction.
3.2.2. Acceleration
4. Speed
4.1. What is it?
4.1.1. The distance an object travels in respects to or per unit of time.
4.1.2. The formula to calculate Speed is Distance over time.
4.2. Instantaneous Speed
4.2.1. The rate or speed of which the object is moving at a specific instant within the total time.
4.3. Average Speed
4.3.1. Is the amount of average speed (rate) throughout a distance.
4.3.2. The Formula for average speed is total distance over total time.
5. Slope
5.1. What is it?
5.1.1. Slope itself is the steepness of a line on a graph.
5.1.2. Slope is calculated by rise over run.
5.1.3. The rate of change can be found by looking at the slope. So the slope can help determine the speed.
