Electromagnetic Radiation
par Andrew Fischenberg
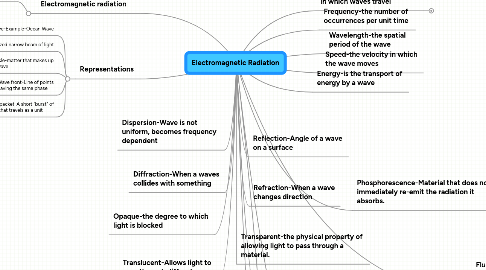

1. Scattering-When a waves collides with something to change its path
1.1. New node
1.1.1. New node
2. Opaque-the degree to which light is blocked
3. Translucent-Allows light to pass through diffusely.
4. Diffraction-When a waves collides with something
5. EMR Spectrum-The range of all possible frequencies in Electromagnetic radiation
5.1. Band/Frequecies and Examples
5.1.1. 10^3-Radio
5.1.2. 10^-2-Microwave
5.1.3. 10^-5-infrared
5.1.4. .5x10^-5-Visible
5.1.5. 10^-8-Ultraviolet
5.1.6. 10^-10-Xray
5.1.7. 10^-12 Gamma Ray
