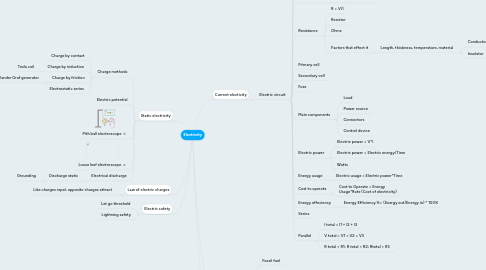
1. Current electicity
1.1. Electric circuit
1.1.1. Circuit breaker
1.1.2. Short circuit
1.1.3. Current/Amps
1.1.3.1. Ammeter
1.1.3.2. Alternating current
1.1.3.3. Direct current
1.1.4. Potential difference/Volts
1.1.4.1. Voltmeter
1.1.5. Resistance
1.1.5.1. R = V/I
1.1.5.2. Resistor
1.1.5.3. Ohms
1.1.5.4. Factors that effect it
1.1.5.4.1. Length, thickness, temperature, material
1.1.6. Primary cell
1.1.7. Secondary cell
1.1.8. Fuse
1.1.9. Main components
1.1.9.1. Load
1.1.9.2. Power source
1.1.9.3. Connectors
1.1.9.4. Control device
1.1.10. Electric power
1.1.10.1. Electric power = V*I
1.1.10.2. Electric power = Electric energy/Time
1.1.10.3. Watts
1.1.11. Energy usage
1.1.11.1. Electric usage = Electric power*Time
1.1.12. Cost to operate
1.1.12.1. Cost to Operate = Energy Usage*Rate (Cost of electricity)
1.1.13. Energy effeciency
1.1.13.1. Energy Efficiency %= (Energy out/Energy in) * 100%
1.1.14. Series
1.1.15. Parallel
1.1.15.1. I total = I1 + I2 + I3
1.1.15.2. V total = V1 = V2 = V3
1.1.15.3. R total < R1; R total < R2; Rtotal < R3
2. Static electricity
2.1. Charge methods
2.1.1. Charge by contact
2.1.2. Charge by induction
2.1.2.1. Tesla coil
2.1.3. Charge by friction
2.1.3.1. Vander Graf generator
2.1.4. Electrostatic series
2.2. Electric potential
2.3. Pith ball electroscope
2.4. Loose leaf electroscope
2.5. Electrical discharge
2.5.1. Discharge static
2.5.1.1. Grounding

