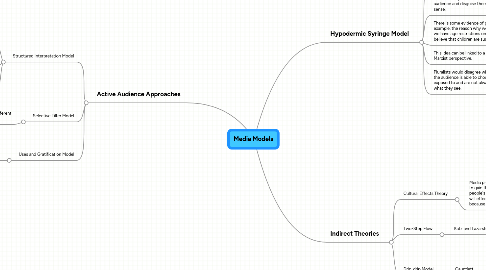
1. Active Audience Approaches
1.1. Structured Interpretation Model
1.1.1. Dominant reading - "obvious" (what the owners want you to accept)
1.1.2. Oppositional reading - disagreeing with the dominant reading
1.1.3. Negotiated reading - somewhere in the middle, taking in both sides of the argument
1.2. Selective Filter Model
1.2.1. Klapper and Fiske - 3 different filters
1.2.1.1. Selection Exposure - what you are shown
1.2.1.2. Perception
1.2.1.3. Retention
1.3. Uses and Gratification Model
1.3.1. Blumler and McQuail
1.3.1.1. individuals are active in their approach to the media and use it as an escape, to gather information, to form relationships, and construct an identity.
2. Hypodermic Syringe Model
2.1. Vance Packard - We are all the same. The audience is inactive and is vulnerable to all media messages.
2.2. People in control of the media e.g. Murdoch, are able to inject their ideologies into the audience and disguise them as common sense.
2.3. There is some evidence of people taking this viewpoint, for example, the reason why we have watersheds on television or why we have age restrictions on films is because the government believe that children are susceptible to negative media messages.
2.4. This idea can be linked to a Marxist perspective.
2.5. Pluralists would disagree with this theory as they believe the audience is able to choose what media they are exposed to and are not always effected so instantly by what they see.
3. Indirect Theories
3.1. Cultural Effects Theory
3.1.1. Media professionals try and appeal to the widest audience possible to gain their consent. This means they need to take into account people's different ethnicities, gender, age etc. because the media will effect them in different ways. This links to Neo-Marxism because
3.2. Two-Step Flow
3.2.1. Katz and Lazarsfeld
3.2.1.1. The status of the "opinion leader" is used to convince you of the media message. This links to hierarchy of credibility where people of high status are asked their opinions on matters. This links to Marxism because it enforces social hierarchy, with those at the top having the most power.
3.3. Drip-drip Model
3.3.1. Gauntlett
3.3.1.1. We are constantly exposed to the same media messages. It helps enforce the message the owners are trying to portray, and it becomes a norm. This links to a Neo-Marxist perspective because it is the dominant class (i.e. white, middle-class men) who have always controlled the content of the media.
