Physics Chapter 16 Static Electricity
da lex wong
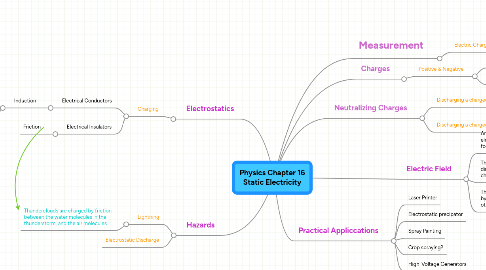

1. Electrostatics
1.1. Charging
1.1.1. Electrical Conductors
1.1.1.1. Induction
1.1.1.1.1. Process of charging a conductor without any contact with the charging body.
1.1.2. Electrical Insulators
1.1.2.1. Friction
2. Hazards
2.1. Lightning
2.1.1. Thunderclouds are charged by friction between the water molecules in the thunderstorm, and the air molecules
2.2. Electrostatic Discharge
3. Charges
3.1. Positive & Negative
3.1.1. Like charges repel
3.1.2. Unlike charges attract
4. Measurement
4.1. Electric Charge
4.1.1. Coulombs (C)
5. Neutralizing Charges
5.1. Discharging a charged insulator
5.1.1. Heat
5.1.2. Humidity
5.2. Discharging a charged conductor
5.2.1. Earthing it (Grounding)
