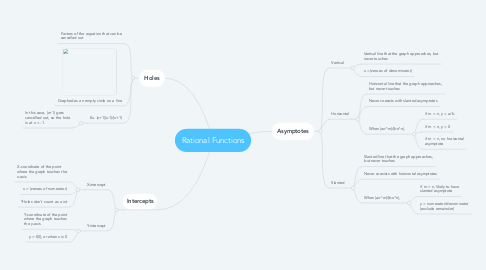
1. Intercepts
1.1. X-intercept
1.1.1. X-coordinate of the point where the graph touches the x-axis
1.1.2. x = (zeroes of numerator)
1.1.3. *Holes don't count as x-int
1.2. Y-intercept
1.2.1. Y-coordinate of the point where the graph touches the y-axis
1.2.2. y = f(0), or when x is 0
2. Holes
2.1. Factors of the equation that can be cancelled out
2.2. Graphed as an empty circle on a line
2.3. Ex. (x+1)(x-1)/(x+1)
2.3.1. In this case, (x+1) gets cancelled out, so the hole is at x = -1.
3. Asymptotes
3.1. Vertical
3.1.1. Vertical line that the graph approaches, but never touches
3.1.2. x = (zeroes of denominator)
3.2. Horizontal
3.2.1. Horizontal line that the graph approaches, but never touches
3.2.2. Never coexists with slanted asymptotes
3.2.3. When (ax^m)/(bx^n),
3.2.3.1. if m = n, y = a/b
3.2.3.2. if m < n, y = 0
3.2.3.3. if m > n, no horizontal asymptote
3.3. Slanted
3.3.1. Slanted line that the graph approaches, but never touches
3.3.2. Never coexists with horizontal asymptotes
3.3.3. When (ax^m)/(bx^n),
3.3.3.1. if m > n, likely to have slanted asymptote
3.3.3.2. y = numerator/denominator (exclude remainder)

