Sustainable supply chain Session#1
by Thomas Potier
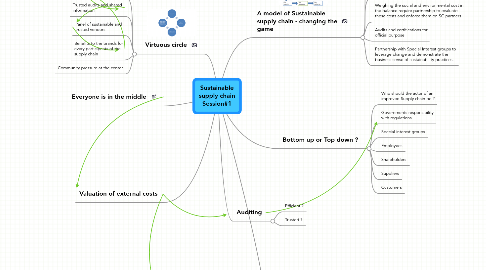
1. Everyone is in the middle
2. Valuation of external costs
3. Share information
3.1. Supply chain efficiency improvement through shared information (Electronic Data Interexchange example)
3.2. Sharing information enables better evaluation of external costs.
3.3. Damaging competition ?
4. Virtuous circle
4.1. Sustainable growth
4.2. Trusted audits and shared information
4.3. Panel of sustainable and trusted vendors
4.4. Benefits to the brands for every participants of the supply chain
4.5. Community pressure at the center
5. Bottom up or Top down ?
5.1. Who should the actor of an improved Supply chain be ?
5.2. Governments responsibility with regulations
5.3. Special interest groups
5.4. Employees
5.5. Shareholders
5.6. Suppliers
5.7. Customers
6. Auditing
6.1. Efficient ?
6.2. Trusted ?
7. A model of Sustainable supply chain - changing the game
7.1. Non sustainable elements of supply chain (red) have traditionnal SC and governement support (Lobbying)
7.2. Organizing the game change requires unusual cooperation and collaborations.
7.3. Weighing the social and environmental cost in the balance require partnership to evaluate these costs and enforce them on SC partners
7.4. Audits and certifications for official purpose
7.5. Partnership with Special Interest groups to leverage change and demonstrate the business sense of sustainability practices.


