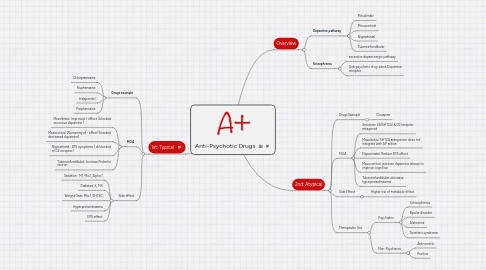
1. 1st: Typical
1.1. Drugs example
1.1.1. Chlorpramazine
1.1.2. Fluphenazine
1.1.3. Haloperidol
1.1.4. Perphenazine
1.2. MOA
1.2.1. Mesolimbic: Improved + effect ( blocked excessive dopamine )
1.2.2. Mesocotical: Worsening of - effect (blocked decreased dopamine)
1.2.3. Nigrostriatal : EPS symptoms ( dt blocked of D2 receptor)
1.2.4. Tuberoinfundibulat: Increase Prolactin neuron
1.3. Side effect
1.3.1. Sedation : M1, Miu1, Alpha 1
1.3.2. Diabetes: X, M3
1.3.3. Weight Gain: Miu 1, 5HT2C
1.3.4. Hyperprolactinaemia
1.3.5. EPS effect
2. Overview
2.1. Dopamine pathway
2.1.1. Mesolimbic
2.1.2. Mesocortical
2.1.3. Nigrastriatal
2.1.4. Tuberoinfundibular
2.2. Scizophrenia
2.2.1. excessive dopaminergic pathway
2.2.2. Anti-psychotic drug: block Dopamine receptor
3. 2nd: Atypical
3.1. Drugs Example
3.1.1. Clozapine
3.2. MOA
3.2.1. Serotonin 2A(5HT2A) & D2 receptor antagonist
3.2.2. Mesolimbic: 5HT2A antagonism does not integrate with AP action
3.2.3. Nigrastriatal: Reduce EPS effect
3.2.4. Mesocortical: increase dopamine release to improve cognitive
3.2.5. Tuberoinfundibular: decrease hyperprolactinaemia
3.3. Side Effect
3.3.1. Higher risk of metabolic effect
3.4. Therapeutic Use
3.4.1. Psychiatric
3.4.1.1. Schizophrenia
3.4.1.2. Bipolar disorder
3.4.1.3. Alzheimeir
3.4.1.4. Tairette's syndrome
3.4.2. Non-Psychiatric
3.4.2.1. Anti-emetic
3.4.2.2. Pruritus

